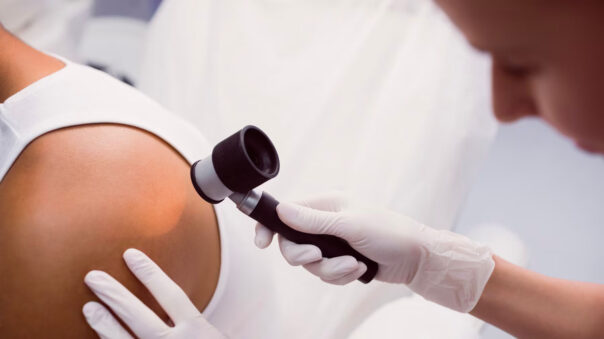
Skin cancer is a pressing global health issue, affecting millions of people worldwide. Recognizing the main types of skin cancer, including Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC), Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC), Melanoma, and Lentigo Melanoma, is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore these diseases in detail, covering their general characteristics, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options.
Additionally, we will introduce you to the innovative Skinive app, which empowers individuals to identify potential skin issues and receive tailored recommendations for their skin’s health. However, it’s important to emphasize that self-medication is not recommended, and consultation with a healthcare professional is essential for diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Skin Cancer: General Overview
Skin cancer is a broad term encompassing various types of malignant neoplasms that develop in the skin. While each type has its unique characteristics, they share the common feature of uncontrolled cell growth that can lead to serious health complications if not promptly addressed.
Common Symptoms of Skin Cancer:
- Changes in the appearance of moles or existing skin lesions.
- The emergence of new skin lesions or growths.
- Irregularities in the color, shape, or size of moles or lesions.
- Moles or lesions that itch, bleed, or crust over.
- Sores that do not heal.
Diagnosis of Skin Cancer: Diagnosing skin cancer typically involves a combination of visual inspection, medical history assessment, and, if necessary, biopsy. Dermatologists use various criteria, such as the ABCDE rule (Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter larger than a pencil eraser, Evolving shape or size), to evaluate moles and skin lesions for potential malignancy.
Treatment Options for Skin Cancer: The choice of treatment depends on the type, stage, and location of the skin cancer. Common treatment modalities include:
- Surgical excision: Removal of the cancerous tissue.
- Mohs surgery: A precise surgical technique for removing skin cancer layer by layer.
- Radiation therapy: The use of targeted radiation to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Medications that destroy cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Medications that stimulate the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
- Targeted therapy: Medications that target specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
Main Types of Skin Cancer:
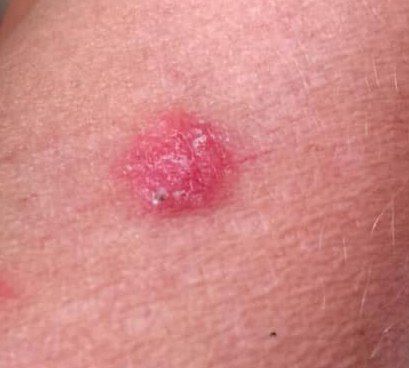
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC):
Squamous cell carcinoma (ICD-10: C44) or SCC originates from squamous cells in the skin’s upper layers, often linked to prolonged sun exposure.
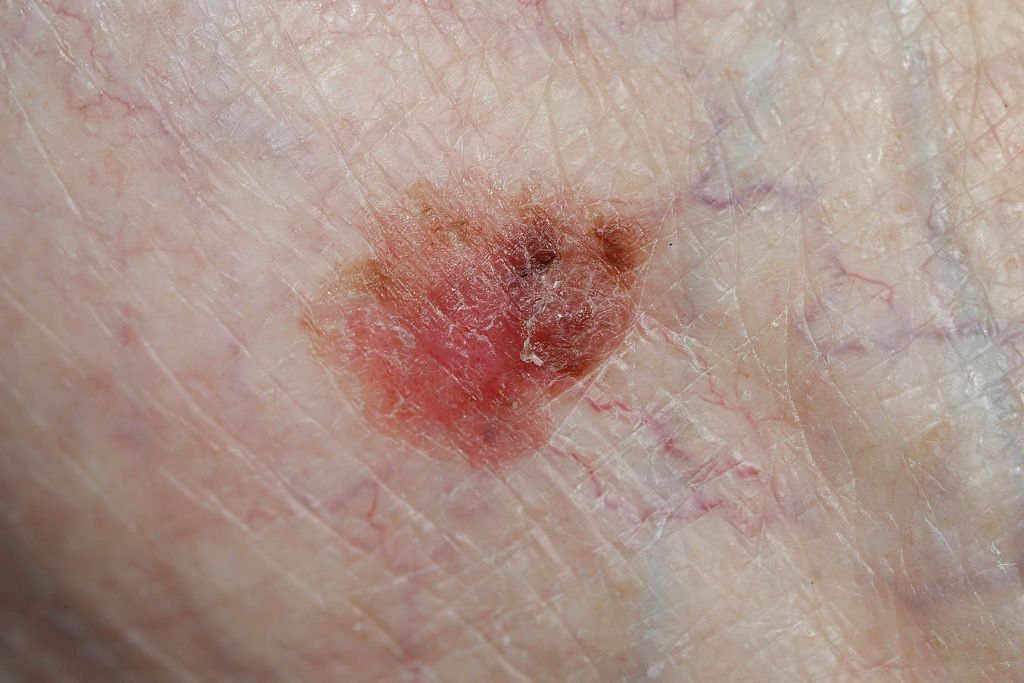
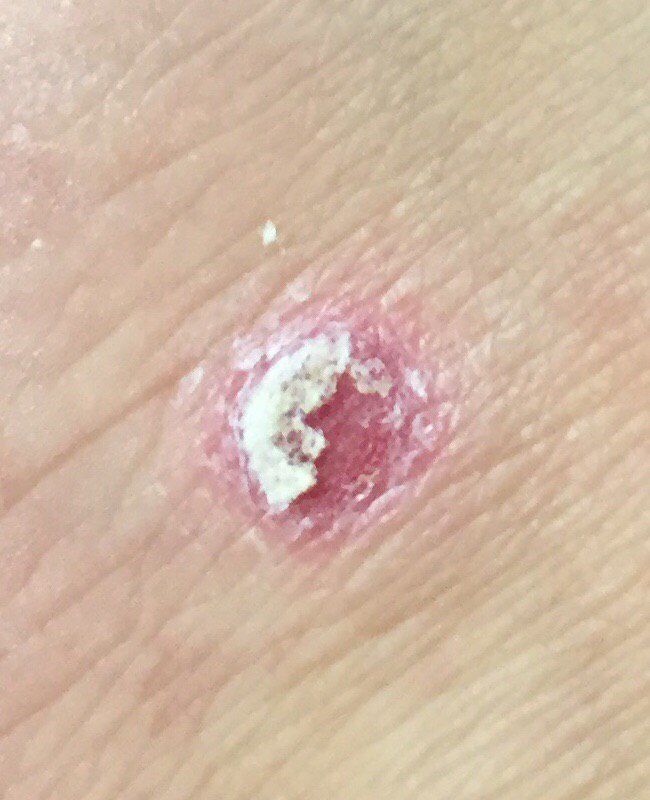
Symptoms: Recognizable by scaly, red patches, open sores, or warts that may bleed or crust. Frequently found on sun-exposed areas.
Diagnosis: Dermatologists perform biopsies to confirm SCC. Early diagnosis is crucial for successful outcomes.
Treatment: Options include surgical removal, Mohs surgery, radiation therapy, and topical medications.
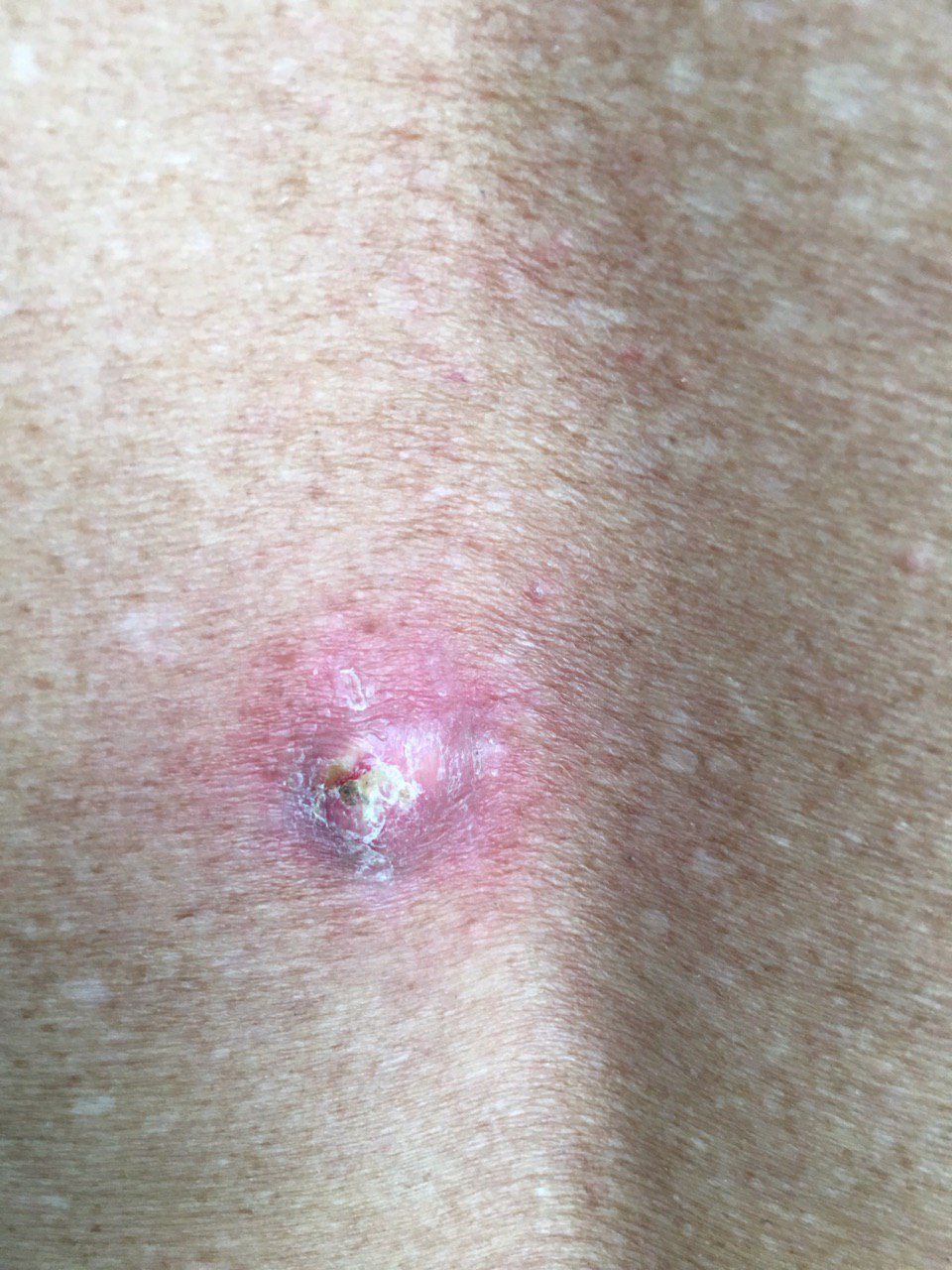
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC):
Basal cell carcinoma (ICD-10: C44) or BCC originates from basal cells in the skin’s lower epidermis, primarily linked to sun exposure.
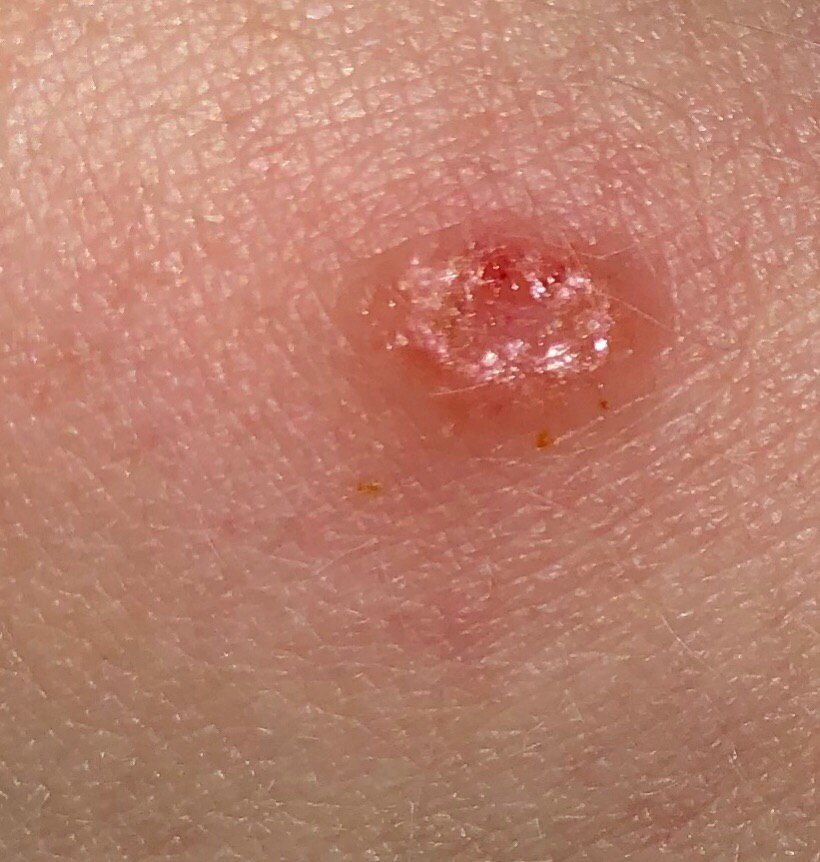
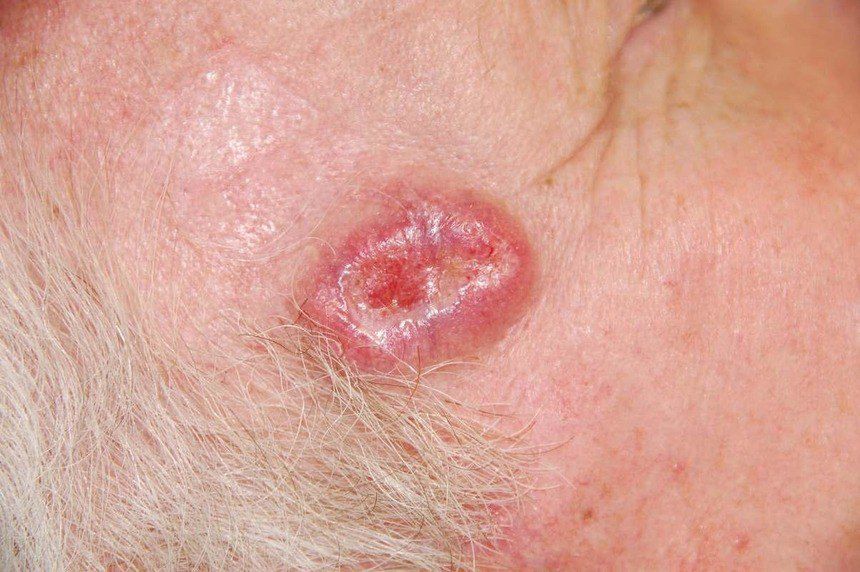
Symptoms: Presents as a pearly bump or a scaly, reddish patch. Slower growth with minimal spread.
Diagnosis: Biopsy confirms BCC. Timely intervention leads to favorable treatment results.
Treatment: Treatment options encompass surgical excision, Mohs surgery, cryotherapy, and topical medications.
Melanoma:
Melanoma arises from melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells, often associated with intense UV exposure.
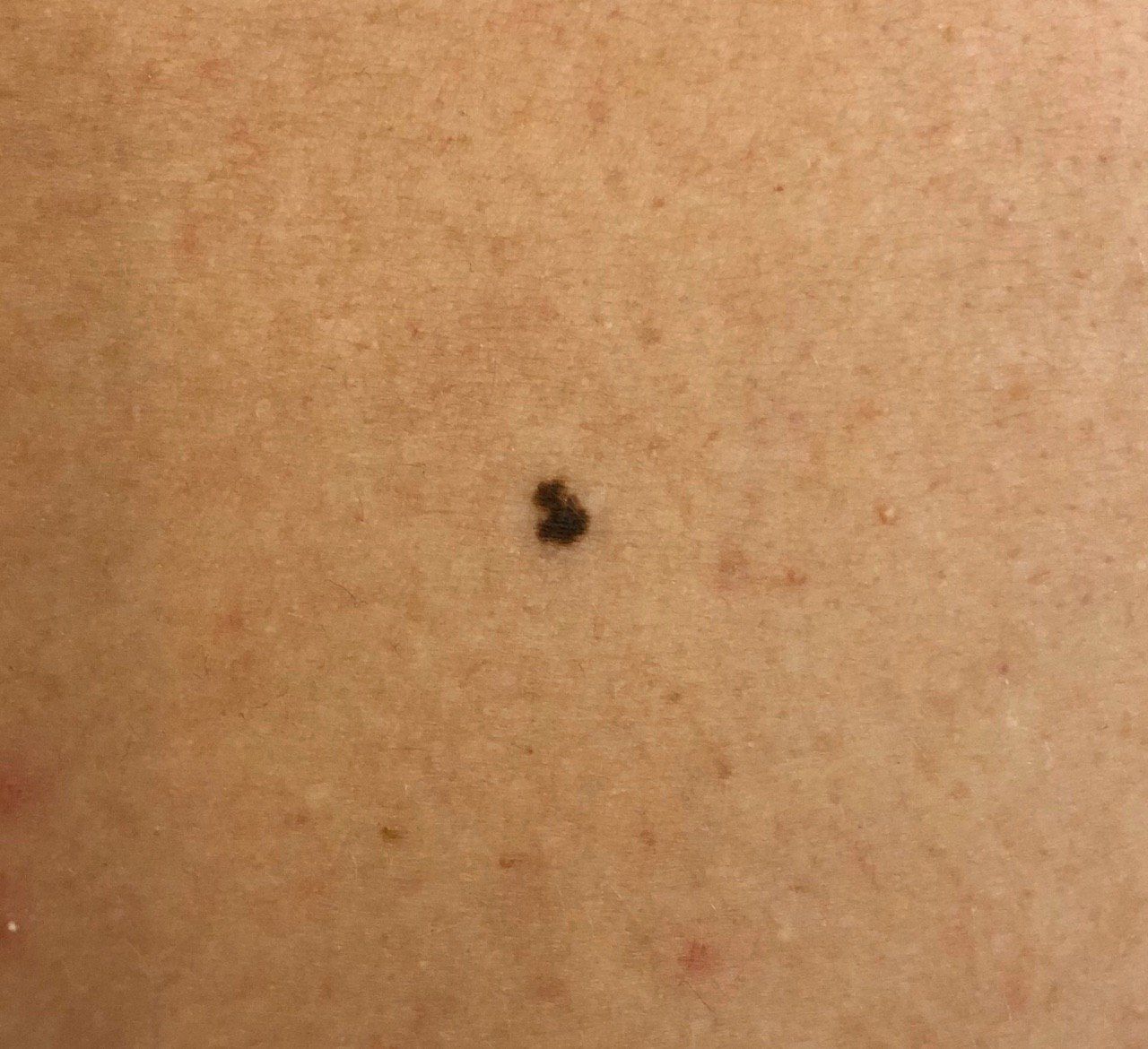

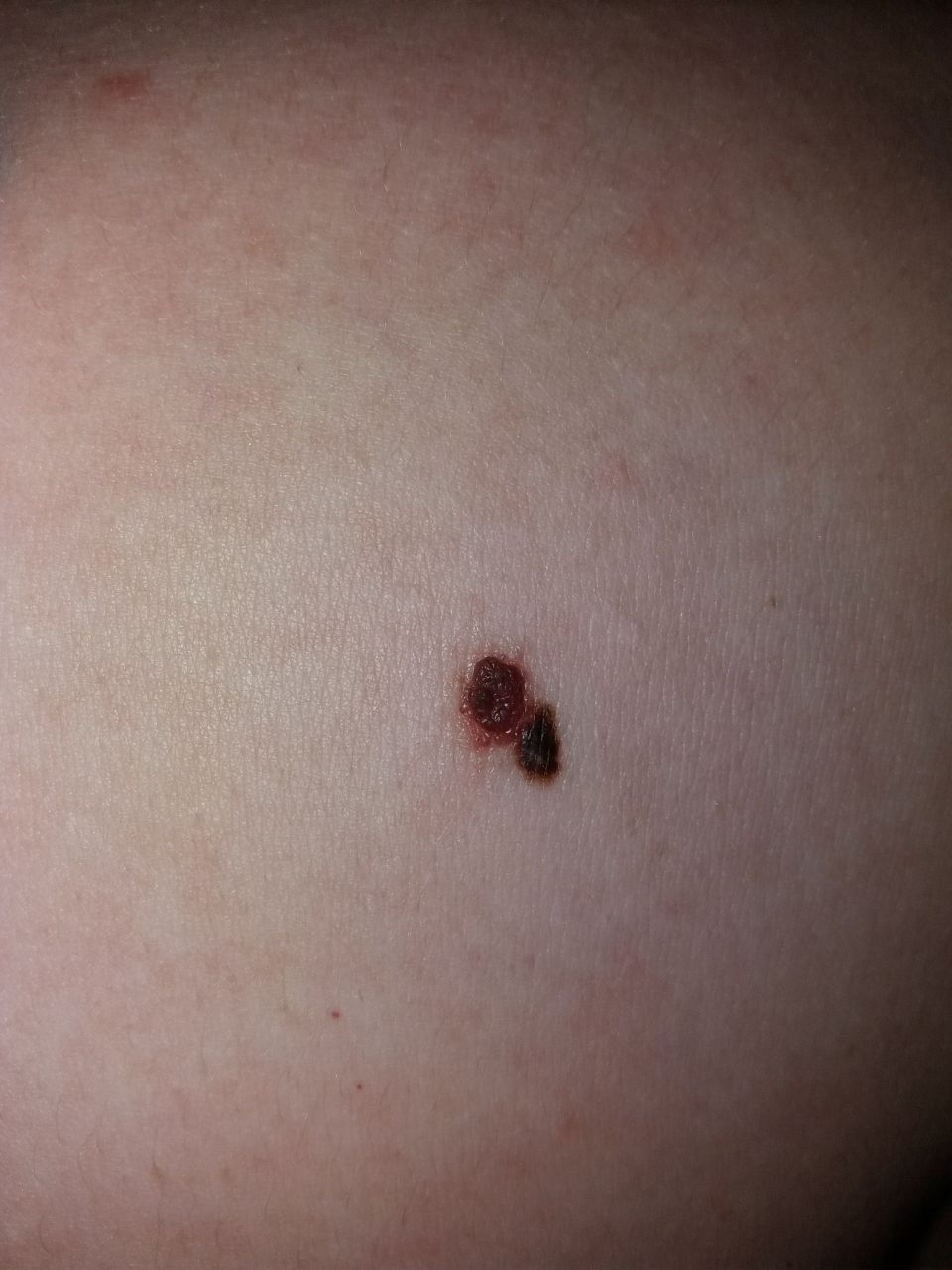
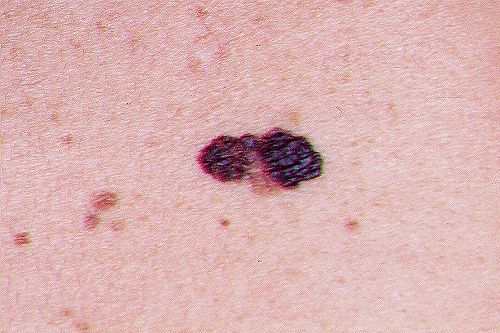
Symptoms: Notable for changing moles with irregular borders, varying colors, or larger diameters.
Diagnosis: Dermatologists use the ABCDE rule (Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, Evolution) and perform biopsies for confirmation.
Treatment: Treatment strategies include surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and radiation.
Lentigo Melanoma:
Lentigo melanoma emerges as an irregularly pigmented patch, primarily on sun-exposed areas.
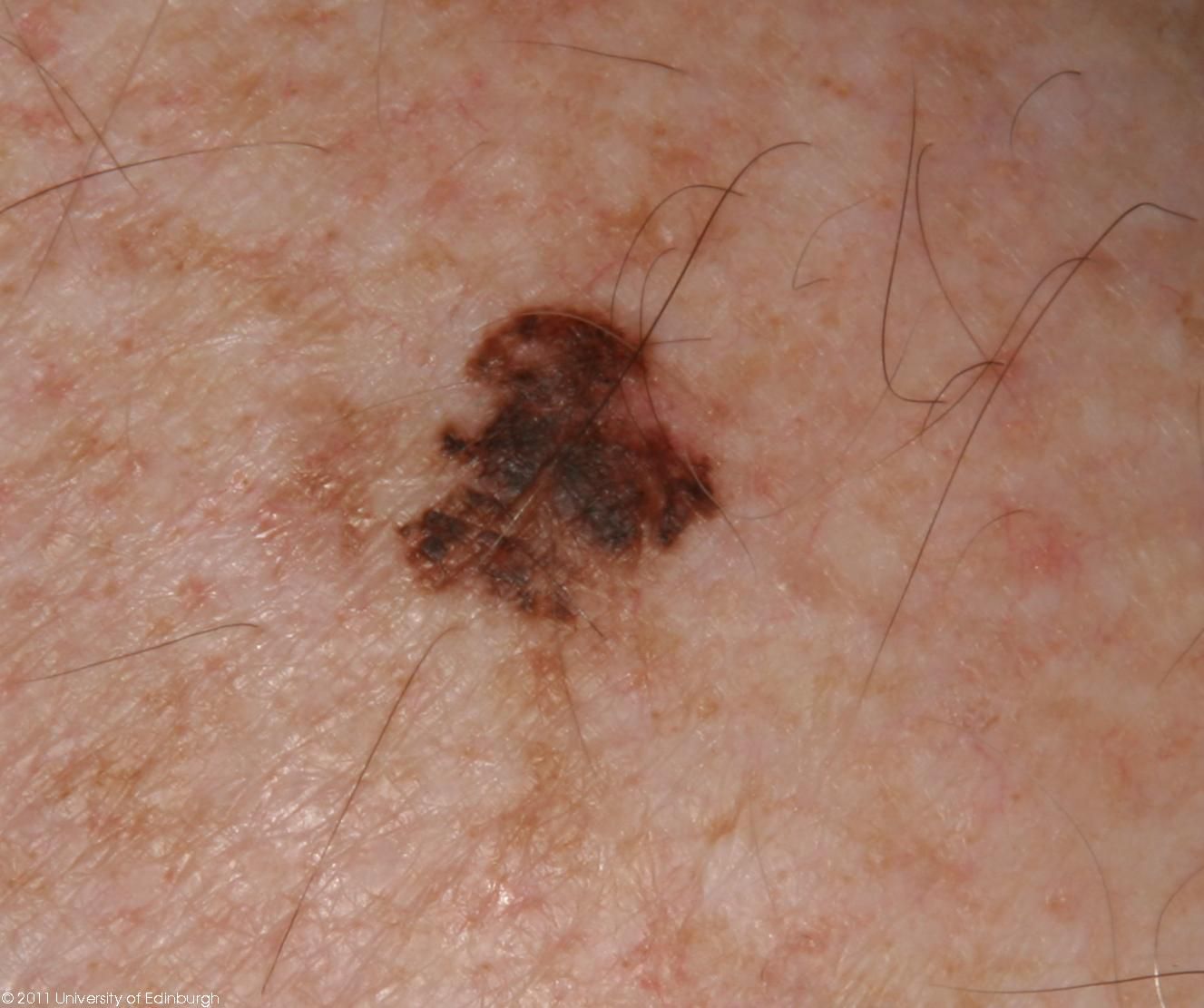
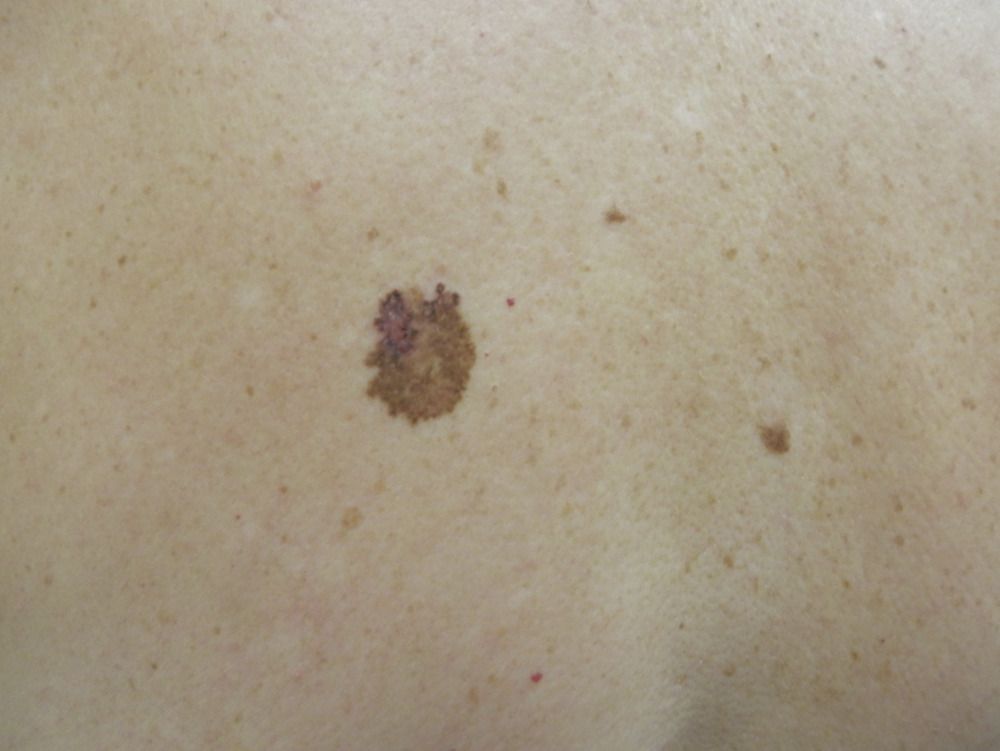
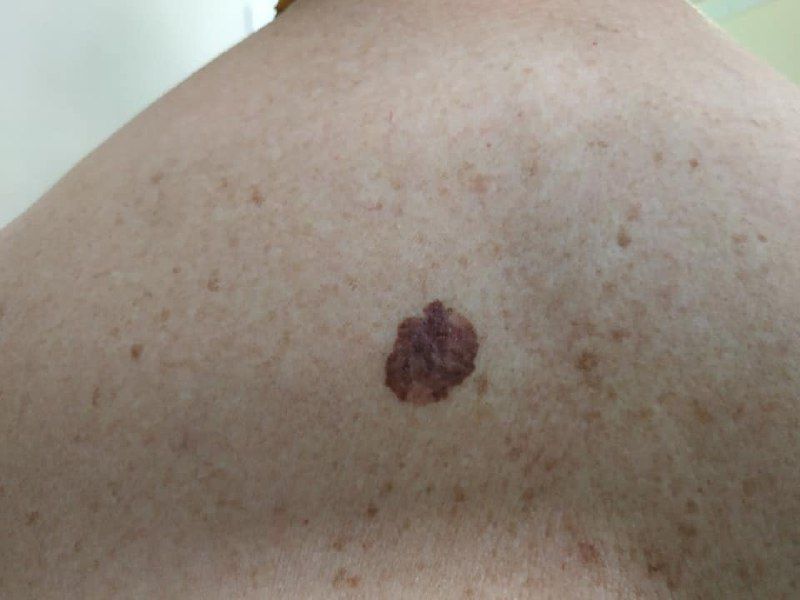
Symptoms: Presents as a slowly enlarging, irregularly pigmented patch.
Diagnosis: Dermatologists conduct examinations and possible biopsies to confirm diagnosis.
Treatment: Early surgical removal is the primary approach for lentigo melanoma.
The Role of Skinive App in Skin Self-exhamination:
The Skinive app serves as a valuable tool to assist in identifying various skin conditions, including potential skin cancers. By capturing an image of a mole or skin lesion, users receive an instant analysis categorizing the condition and offering essential insights. While Skinive can provide preliminary information, it should never replace professional medical advice. Dermatologists possess the expertise to perform comprehensive evaluations and biopsies when necessary. However, Skinive complements their efforts by providing initial information and continuous monitoring of skin health.
Conclusion:
Skin cancer is a formidable adversary, but knowledge and vigilance can lead to early detection and successful outcomes. Understanding the types, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options is pivotal in safeguarding your skin health. The Skinive app stands as an ally, aiding users in monitoring their skin health and providing preliminary insights. However, it should always work in harmony with the expertise of dermatologists. Your skin’s well-being is a priority, deserving professional attention and care.
Take the first step towards healthier skin today by downloading the free Skinive app in AppStore or GooglePlay . While it equips you with initial information, remember that it should enhance rather than replace the role of seasoned medical professionals. Responsible skin health management necessitates vigilant observation and regular consultations with dermatologists.