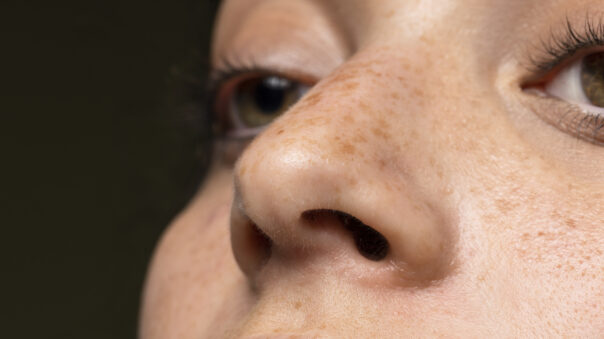
Skin pigmentation and discoloration are common concerns that affect people of all ages and skin types. These conditions can arise due to various factors, including genetics, sun exposure, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions. Understanding the different types of skin pigmentation and discoloration is crucial for effective prevention and treatment strategie
Types of Skin Pigmentation and Discoloration:
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation refers to the darkening of the skin in certain areas. It occurs when there is an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Common types of hyperpigmentation include:
- Sunspots or Age Spots (Actinic keratosis): Result from prolonged sun exposure and usually appear on areas frequently exposed to sunlight, such as the face, hands, and shoulders.
- Melasma: Often triggered by hormonal changes, such as pregnancy or birth control pills. Melasma presents as brown or grayish patches, typically on the face.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): Develops after inflammation or injury to the skin, such as acne scars or insect bites.
Hypopigmentation
Hypopigmentation is the loss of skin color, resulting in lighter patches compared to the surrounding skin. It occurs when there is a decrease in melanin production or distribution. Common types include:
- Vitiligo: An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks melanocytes, leading to depigmented patches on the skin.
- Albinism: A genetic condition characterized by the absence or reduction of melanin production, resulting in very light skin, hair, and eyes.
- Tinea Versicolor: A fungal infection that disrupts melanin production, causing patches of lighter or darker skin.
Vascular Discoloration
Vascular discoloration occurs due to abnormalities in blood vessels, leading to red, purple, or blue discoloration. Common types include:
- Rosacea: A chronic skin condition characterized by redness, flushing, and visible blood vessels, typically affecting the face.
- Spider Veins: Small, dilated blood vessels that appear close to the surface of the skin, often on the legs or face.
- Hemangiomas: Benign growths of blood vessels that can appear as red or purple birthmarks.
Prevention of Skin Pigmentation and Discoloration
Preventing skin pigmentation and discoloration involves adopting healthy skincare practices and minimizing exposure to potential triggers. Here are some preventive measures:
- Sun Protection: Wear broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily, seek shade, and wear protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses to shield the skin from harmful UV rays.
- Avoid Irritants: Use gentle skincare products suitable for your skin type and avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive treatments that can cause inflammation and pigmentation issues.
- Manage Hormonal Changes: For conditions like melasma, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate management of hormonal fluctuations, especially during pregnancy or when using oral contraceptives.
- Treat Skin Conditions Promptly: Address inflammatory skin conditions such as acne promptly to minimize the risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Treatment of Skin Pigmentation and Discoloration
Effective treatment of skin pigmentation and discoloration depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Treatment options may include:
- Topical Agents: Prescription creams containing ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, kojic acid, or vitamin C can help lighten dark spots and even out skin tone.
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels containing alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), or trichloroacetic acid (TCA) can exfoliate the skin and reduce pigmentation.
- Laser Therapy: Various laser treatments, such as intense pulsed light (IPL), fractional lasers, and Q-switched lasers, can target pigmented lesions, stimulate collagen production, and improve overall skin tone.
- Microdermabrasion and Dermabrasion: These procedures involve mechanical exfoliation to remove the outer layer of the skin, revealing smoother, more evenly pigmented skin underneath.
- Surgical Interventions: In cases of severe hypopigmentation or vascular discoloration, surgical procedures like skin grafting or vascular laser treatments may be necessary.
In conclusion, skin pigmentation and discoloration are multifaceted issues that require a tailored approach to prevention and treatment. By understanding the different types of pigmentation and adopting preventive measures, individuals can maintain healthy, radiant skin. For those already experiencing pigmentation concerns, consulting a dermatologist is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for achieving clearer, more even-toned skin.
Changes in skin tone can be concerning, but effective treatments and support are available. Don’t hesitate to seek guidance from healthcare professionals or therapists. Remember, you’re not alone, and there are solutions to help you navigate through skin-related challenges.
Discover the path to beautiful skin with the Skinive app. Download now and uncover personalized skincare insights to achieve your radiant potential.